J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 666-670 (2014)
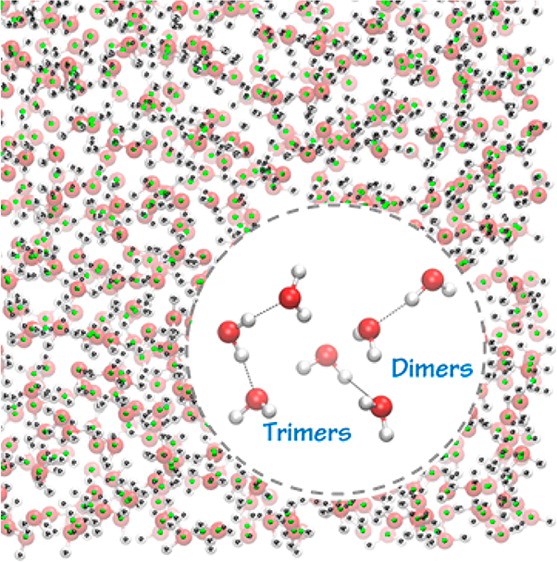
It is important to test methods for simulating water, but small water clusters for which benchmarks are available are not very representative of the bulk. Here we present benchmark calculations, in particular CCSD(T) calculations at the complete basis set limit, for water 26-mers drawn from Monte Carlo simulations of bulk water. These clusters are large enough that each water molecule participates in 2.5 hydrogen bonds on average. The electrostatically embedded three-body approximation with CCSD(T) embedded dimers and trimers reproduces the relative binding energies of eight clusters with a mean unsigned error (MUE, kcal per mole of water molecules) of only 0.009 and 0.015 kcal for relative and absolute binding energies, respectively. Using only embedded dimers (electrostatically embedded pairwise approximation) raises these MUEs to 0.038 and 0.070 kcal, and computing the energies with the M11 exchange-correlation functional, which is very economical, yields errors of only 0.029 and 0.042 kcal.