Langmuir 32, 2093-2101 (2016)
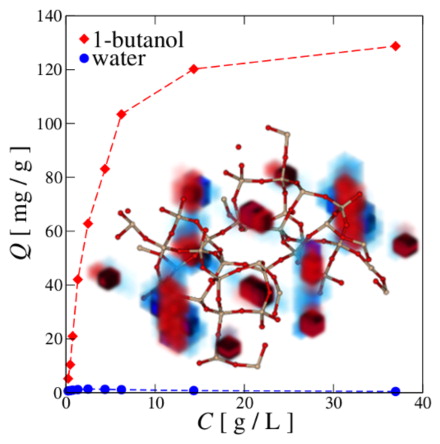
Anaerobic fermentation can transform carbohydrates to yield a multicomponent mixture comprising mainly of acetone, 1-butanol, and ethanol (ABE) in a typical weight ratio of 3:6:1. Compared to ethanol, 1-butanol, the main product of ABE fermentation, offers significant advantages as a biofuel or a fuel additive. However, the toxicity of 1-butanol for cell cultures requires broth concentrations to be low in 1-butanol (≈1–2 wt %). An energy-efficient recovery method that performs well even at low 1-butanol concentrations is therefore necessary to ensure economic feasibility of the ABE fermentation process. In this work, configurational-bias Monte Carlo simulations in the Gibbs ensemble are performed to probe the adsorption of 1-butanol/water solutions onto all-siliceous zeolites with the framework types MFI and FER. At low solution concentration, the selectivity and capacity for 1-butanol in MFI are larger than those in FER, while the opposite is true for concentrations at or above those of ABE broths. Structural analysis at various loadings sheds light on the different sorbate–sorbate and sorbate–sorbent interactions that govern trends in adsorption in each zeolite.