Chem. Theor. Comp. 3, 350-357 (2007)
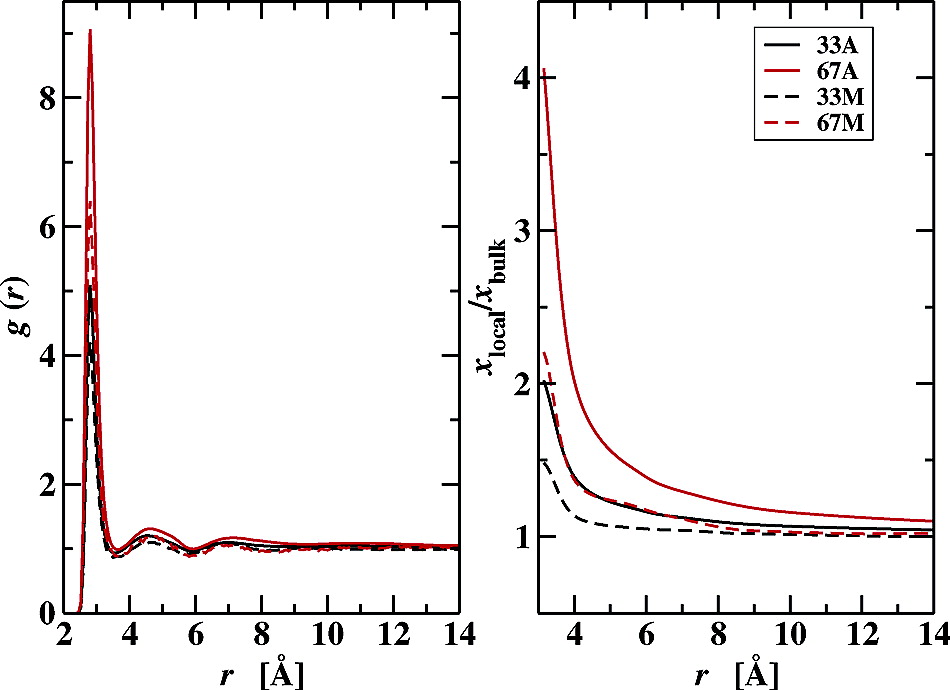
To investigate conformational properties of an isolated n-octadecane chain solvated in water−acetonitrile mixtures, configurational-bias Monte Carlo simulations in the isobaric−isothermal ensemble were performed at T = 323 K and p = 10 atm. The united-atom version of the transferable potentials for phase equilibria force field was used to represent n-octadecane and acetonitrile, and the TIP-4P model was used for water. In all four environments (neat water, 33 and 67 mole percent acetonitrile, and neat acetonitrile), similar conformational distributions are observed as in a previous study for water−methanol solvent mixtures; that is, the n-octadecane chain is found to predominantly adopt extended but not all-trans conformations, and only a small fraction of more collapsed conformations is observed for aqueous hydration, water-rich solvent environments. Analysis of the local solvation structures in the water−acetonitrile mixtures shows an enrichment of the acetonitrile molecules near the methylene and methyl segments of the n-octadecane chain. However, upon increasing the concentration of acetonitrile, the enhancement of acetonitrile and the depletion of water is more pronounced than for water−methanol mixtures because of the weaker interactions between acetonitrile and water.