Publications 2000 - 2009
[99] Vapor-liquid equilibria of water from first principles: Comparison of density functionals and basis sets
Mol. Phys. 104, 3619-3626 (2006)
[98] Phase Behavior of Elemental Aluminum Using Monte Carlo Simulations
J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 26135-26142 (2006)
[97] Time-Dependent Properties of Liquid Water: A Comparison of Car−Parrinello and Born−Oppenheimer Molecular Dynamics Simulations
J. Chem. Theor. Comp. 2, 1274-1281 (2006)
[96] Retention in gas-liquid chromatography with a polyethylene oxide stationary phase: Molecular simulation and experiment
J. Chromatogr. A 1126, 373-380 (2006)
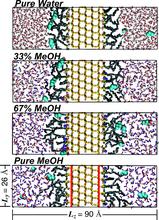
[95] Chain conformation and solvent partitioning in reversed-phase liquid chromatography: Monte Carlo simulations for various water/methanol concentrations
J. Chromatogr. A 1126, 219-231 (2006)
[94] Monte Carlo Calculations for the Solid-State Properties of Warfarin Sodium 2-Propanol Solvate
Cryst. Growth Des. 6, 1318-1323 (2006)
[93] Conformation and Solvation Structure for an Isolated n-Octadecane Chain in Water, Methanol, and Their Mixtures
J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 10519-10525 (2006)
[92] Direct calculation of Henry's law constants from Gibbs ensemble Monte Carlo simulations: Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and methane in ethanol
Theor. Chem. Acc. 115, 391-397 (2006)
[91] Viscous Water Meniscus under Nanoconfinement
Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, art. no. 177803/4 pages (2006)
[90] Critical Properties of Aluminum
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 4224-4225 (2006)
[89] Structure and Dynamics of the Aqueous Liquid−Vapor Interface: A Comprehensive Particle-Based Simulation Study
J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 3738-3746 (2006)
[88] Microscopic Structure and Solvation in Dry and Wet Octanol
J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 3555-3563 (2006)
[87] Simulating Fluid-Phase Equilibria of Water from First Principles
J. Phys. Chem. A 110, 640-646 (2006)
[86] Transferable Potentials for Phase Equilibria. 8. United-Atom Description for Thiols, Sulfides, Disulfides, and Thiophene
J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 24100-24107 (2005)
[85] Effects of Conformational Distributions on Sigma Profiles in COSMO Theories
J. Phys. Chem. A 109, 1-6 (2005)
[84] Partial Molar Volume and Solvation Structure of Naphthalene in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide: A Monte Carlo Simulation Study
J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 19885-19892 (2005)
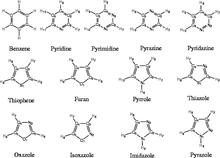
[83] Transferable Potentials for Phase Equilibria. 7. Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Amines, Nitroalkanes and Nitrobenzene, Nitriles, Amides, Pyridine, and Pyrimidine
J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 18974-18982 (2005)
[82] Isobaric–Isothermal Monte Carlo Simulations from First Principles: Application to Liquid Water at Ambient Conditions
ChemPhysChem 6, 1894-1901 (2005)
[81] Microscopic Origins for the Favorable Solvation of Carbonate Ether Copolymers in CO2
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 12338-12342 (2005)
[80] Temperature Dependence of Hydrogen Bonding: An Investigation of the Retention of Primary and Secondary Alcohols in Gas−Liquid Chromatography
J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 15118-15125 (2005)
[79] A molecular simulation study of the bonded-phase structure in reversed-phase liquid chromatography with neat aqueous solvent
J. Chromatogr. A 1079, 127-135 (2005)
[78] Elucidating the Vibrational Spectra of Hydrogen-Bonded Aggregates in Solution: Electronic Structure Calculations with Implicit Solvent and First-Principles Molecular Dynamics Simulations with Explicit Solvent for 1-Hexanol in n-Hexane
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 4722-4729 (2005)
[77] Vapor−Liquid and Vapor−Solid Phase Equilibria for United-Atom Benzene Models near Their Triple Points: The Importance of Quadrupolar Interactions
J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 5368-5374 (2005)
[76] Simulating Vapor−Liquid Nucleation of Water: A Combined Histogram-Reweighting and Aggregation-Volume-Bias Monte Carlo Investigation for Fixed-Charge and Polarizable Models
J. Phys. Chem. A 109, 1137-1145 (2005)
[75] Pressure Dependence of the Vapor−Liquid−Liquid Phase Behavior in Ternary Mixtures Consisting of n-Alkanes, n-Perfluoroalkanes, and Carbon Dioxide
J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 2911-2919 (2005)
[74] Simulating the vapour-liquid equilibria of large cyclic alkanes
Mol. Phys. 103, 99-104 (2005)
[73] Transferable Potentials for Phase Equilibria. 6. United-Atom Description for Ethers, Glycols, Ketones, and Aldehydes
J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 17596-17605 (2004)
[72] Liquid Water from First Principles: Investigation of Different Sampling Approaches
J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 12990-12998 (2004)
[71] Binary phase behavior and aggregation of dilute methanol in supercritical carbon dioxide: A Monte Carlo simulation study
J. Chem. Phys. 121, 1525-1534 (2004)
[70] Simulation Studies on the Effects of Mobile-Phase Modification on Partitioning in Liquid Chromatography
Anal. Chem. 76, 2886-2892 (2004)
[69] Vapor−Liquid and Vapor−Solid Phase Equilibria of Fullerenes: The Role of the Potential Shape on the Triple Point
J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 12320-12323 (2003)
[68] Temperature Dependence of Transfer Properties: Importance of Heat Capacity Effects
J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 10623-10627 (2003)
[67] Simulating the Nucleation of Water/Ethanol and Water/n-Nonane Mixtures: Mutual Enhancement and Two-Pathway Mechanism
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 3113-3118 (2003)
[66] Vapor−Liquid Interfacial Properties of Mutually Saturated Water/1-Butanol Solutions
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 12232-12237 (2002)
[65] Vapor-liquid phase equilibria of triacontane isomers: deviations from the principle of corresponding states
Fluid Phase Equil. 202, 307-324 (2002)
[64] Vapor−Liquid Phase Equilibria for Linear and Branched Alkane Monolayers Physisorbed on Au(111)
Langmuir 18, 6088-6095 (2002)
[63] Molecular Simulation of Concurrent Gas−Liquid Interfacial Adsorption and Partitioning in Gas−Liquid Chromatography
Anal. Chem. 74, 3518-3524 (2002)
[62] Temperature effects on the retention of n-alkanes and arenes in helium–squalane gas–liquid chromatography: Experiment and molecular simulation
J. Chromatogr. A 954, 181-190 (2002)
[61] Aggregation in Dilute Solutions of 1-Hexanol in n-Hexane: A Monte Carlo Simulation Study
J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 3968-3978 (2002)
[60] Simulating vapor–liquid nucleation of n-alkanes
J. Chem. Phys. 116, 4317-4329 (2002)
[59] Influence of Analyte Overloading on Retention in Gas−Liquid Chromatography: A Molecular Simulation View
Anal. Chem. 74, 37-44 (2002)
[58] Aggregation-volume-bias Monte Carlo simulations of vapor-liquid nucleation barriers for Lennard-Jonesium
J. Chem. Phys. 115, 10903-10913 (2001)
[57] Improving the Efficiency of the Aggregation−Volume−Bias Monte Carlo Algorithm
J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 11275-11282 (2001)
[56] Simulation Studies of Retention in Isotropic or Oriented Liquid n-Octadecane
J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 10961-10966 (2001)
[55] Direct Gibbs Ensemble Monte Carlo Simulations for Solid−Vapor Phase Equilibria: Applications to Lennard−Jonesium and Carbon Dioxide
J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 9840-9848 (2001)
[54] Surface Coverages of Bonded-Phase Ligands on Silica: A Computational Study
Anal. Chem. 73, 4006-4011 (2001)
[53] Monte Carlo Calculations for Alcohols and Their Mixtures with Alkanes. Transferable Potentials for Phase Equilibria. 5. United-Atom Description of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols
J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 3093-3104 (2001)
[52] Vapor-liquid equilibria of mixtures containing alkanes, carbon dioxide and nitrogen
AIChE J. 47, 1676-1682 (2001)
[51] Functional self similarity, scaling and a renormalization group calculation of the partition function for a non-ideal chain
Physica A 289, 107-136 (2001)
[50] Effect of Branching on the Fluid Phase Behavior of Alkane Monolayers
Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3460-3463 (2000)
[49] A Novel Monte Carlo Algorithm for Simulating Strongly Associating Fluids: Applications to Water, Hydrogen Fluoride, and Acetic Acid
J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 8725-8734 (2000)
[48] Self-Adapting Fixed-End-Point Configurational-Bias Monte Carlo Method for the Regrowth of Interior Segments of Chain Molecules with Strong Intramolecular Interactions
Macromolecules 33, 7207-7218 (2000)
[47] Transferable potentials for phase equilibria. 4. United-atom description of linear and branched alkenes and of alkylbenzenes
J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 8008-8016 (2000)
[46] Partitioning of Alkane and Alcohol Solutes between Water and (Dry or Wet) 1-Octanol
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 6464-6467 (2000)
[45] Molecular structure and phase diagram of the binary mixture of n-heptane and supercritical ethane: A Gibbs-ensemble Monte Carlo study
J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 2415-2423 (2000)
[44] Development of Polarizable Water Force Fields for Phase Equilibrium Calculations
J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 2391-2401 (2000)
[43] Adiabatic Nuclear and Electronic Sampling Monte Carlo Simulations in the Gibbs Ensemble: Application to Polarizable Force Fields for Water
J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 2378-2390 (2000)
[132] Web-based Visualization and Analysis of Atmospheric Nucleation Processes
International Journal of u- and e- Service, Science and Technology 2, 25-38 (2009)
[131] Monte Carlo Simulations of Binary Mixtures of Nitrotoluene Isomers with n-Decane
J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 13752-13760 (2009)
[130] Isobaric-Isothermal Molecular Dynamics Simulations Utilizing Density Functional Theory: An Assessment of the Structure and Density of Water at Near-Ambient Conditions
J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 11959-11964 (2009)
[129] Vapor-liquid phase equilibria of water modelled by a Kim-Gordon potential
Chem. Phys. Lett. 479, 60-64 (2009)
[128] Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Nanoclusters Controlling Gas-to-Particle Nucleation
J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 10354-10370 (2009)
[127] TraPPE-UA Force Field for Acrylates and Monte Carlo Simulations for Their Mixtures with Alkanes and Alcohols
J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 6415-6425 (2009)
[126] Exploring the Formation of Multiple Layer Hydrates for a Complex Pharmaceutical Compound
J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 5929-5937 (2009)
[125] Self-Consistent Polarization Density Functional Theory: Application to Argon
J. Phys. Chem. A 113, 2075-2085 (2009)
[124] Bond Angle Distributions of Carbon Dioxide in the Gas, Supercritical, and Solid Phases
J. Phys. Chem. A 113, 2053-2059 (2009)
[123] The effects of chain length, embedded polar groups, pressure, and pore shape on structure and retention in reversed-phase liquid chromatography: Molecular-level insights from Monte Carlo simulations
J. Chromatogr. A 1216, 2320-2331 (2009)
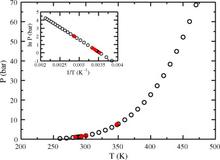
[122] Monte Carlo simulations of 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene (TATB): Pressure and temperature effects for the solid phase and vapor-liquid phase equilibria
J. Chem. Phys. 129, art. no. 194510/8 pages (2008)
[121] Development of the TraPPE-UA force field for ethylene oxide
Fluid Phase Equil. 274, 44-49 (2008)
[120] Importance of the Number of Acid Molecules and the Strength of the Base for Double-Ion Formation in (H2SO4)m·Base·(H2O)6 Clusters
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 14144-14147 (2008)
[119] Structure and Speciation in Hydrous Silica Melts. 2. Pressure Effects
J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 13015-13021 (2008)
[118] Structure and Speciation in Hydrous Silica Melts. 1. Temperature and Composition Effects
J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 13005-13014 (2008)
[117] Structure of the Methanol Liquid−Vapor Interface: A Comprehensive Particle-Based Simulation Study
J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 15412-15418 (2008)
[116] Solubility in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide: Importance of the Poynting Correction and Entrainer Effects
J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 11374-11380 (2008)
[115] Influence of bonded-phase coverage in reversed-phase liquid chromatography via molecular simulation. II. Effects on solute retention
J. Chromatogr. A 1204, 20-27 (2008)
[114] Influence of bonded-phase coverage in reversed-phase liquid chromatography via molecular simulation. I. Effects on chain conformation and interfacial properties
J. Chromatogr. A 1204, 11-19 (2008)
[113] Molecular-Level Comparison of Alkylsilane and Polar-Embedded Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography Systems
Anal. Chem. 80, 6214-6221 (2008)
[112] Excited State Hydrogen Bond Dynamics: Coumarin 102 in Acetonitrile−Water Binary Mixtures
J. Phys. Chem. A 112, 2511-2514 (2008)
[111] Application of the TraPPE Force Field for Predicting the Hildebrand Solubility Parameters of Organic Solvents and Monomer Units
J. Chem. Theor. Comp. 4, 136-144 (2008)
[110] Size Effects on the Solvation of Anions at the Aqueous Liquid−Vapor Interface
J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 210-218 (2008)
[109] Free Energies of Formation of Metal Clusters and Nanoparticles from Molecular Simulations: Aln with n = 2−60
J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 16227-16242 (2007)
[108] Pressure Dependence of the Hildebrand Solubility Parameter and the Internal Pressure: Monte Carlo Simulations for External Pressures up to 300 MPa
J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 15634-15641 (2007)
[107] Prediction of viscosities and vapor-liquid equilibria for five polyhydric alcohols by molecular simulation
Fluid Phase Equil. 260, 218-231 (2007)
[106] Prediction of the bubble point pressure for the binary mixture of ethanol and 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane from Gibbs ensemble Monte Carlo simulations using the TraPPE force field
Fluid Phase Equil. 260, 199-211 (2007)
[105] Application of the TraPPE Force Field to Predicting Isothermal Pressure–Volume Curves at High Pressures and High Temperatures
Intl. J. Thermophys. 28, 3301-3306 (2007)
[104] Transferable Potentials for Phase Equilibria. 9. Explicit Hydrogen Description of Benzene and Five-Membered and Six-Membered Heterocyclic Aromatic Compounds
J. Phys. Chem. B 111, 10790-10799 (2007)
[103] Retention Mechanism in Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography: A Molecular Perspective
Anal. Chem. 79, 6551-6558 (2007)
[102] Spatial correlation of dipole fluctuations in liquid water
Mol. Phys. 105, 1411-1417 (2007)
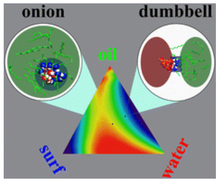
[101] Dumbbells and onions in ternary nucleation
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9, 2779-2781 (2007)
[100] Monte Carlo Simulations of an Isolated n-Octadecane Chain Solvated in Water−Acetonitrile Mixtures
Chem. Theor. Comp. 3, 350-357 (2007)
[R20] Web-Based Visualization of Atmospheric Nucleation Processes Using Java3D
in "Proceedings of the 2009 9th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster Computing and the Grid", CCGRID '09 IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, 2009, pp. 597-602
[R19] Large‐Scale Monte Carlo Simulations for Aggregation, Self‐Assembly, and Phase Equilibria
in "Multiscale Simulation Methods for Nanomaterials" Eds. R.B. Ross and S. Mohanty, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, 2008, pp. 189-200
[R18] Aluminum Nanoparticles: Accurate Potential Energy Functions and Physical Properties
in “Large Scale Molecular Dynamics, Nanoscale and Mesoscale Modeling and Simulation,” pp. 169–188, eds. R.B. Ross and S. Mohanty (Wiley, Hoboken, 2008)
[R17] Molecular Simulation Approaches to Solubility
in “Developments and Applications in Solubility,” pp. 171-187, ed. T.M. Letcher (Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2007)
[R16] Toward a Monte Carlo program for simulating vapor-liquid phase equilibria from first principles
Comput. Phys. Commun. 169, 289-294 (2005)
[R15] Challenges in the development of transferable force fields for phase equilibrium calculations
in "Report on Forum 2000: Fluid Properties for New Technologies, Connecting Virtual Design with Physical Reality", NIST Special Publications, Vol. 975 Eds. J.C. Rainwater, D.G. Friend, H.H.J.M. Hanley, A.H. Harvey, C.D. Holcomb, A. Laesecke, J. Magee, and C. Muzny, NIST: Boulder, CO, 2001, pp. 110-112
[R14] Simulating retention in gas-liquid chromatography: Benzene, toluene, and xylene solutes
Intl. J. Thermophys. 22, 111-122 (2001)
[R13] Monte Carlo calculations for the phase equilibria of alkanes, alcohols, water, and their mixtures
Fluid Phase Equil. 183-184, 301-309 (2001)
[R12] Exploring multicomponent phase equilibria by Monte Carlo simulations: Towards a description of gas-liquid chromatography
ACS Symposium Series, Vol. 748 Eds. J.F. Parcher and T.L. Chester, ACS Books: Washington, DC, 2000, pp. 82-95