J. Phys. Chem. A 113, 2075-2085 (2009)
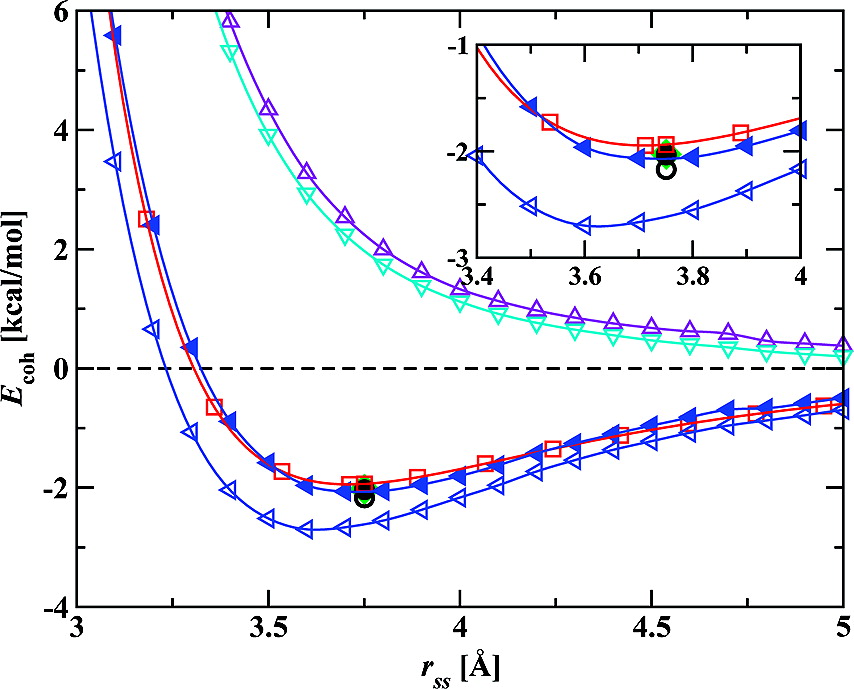
We present a comprehensive set of results for argon, a case study in weak interactions, using the self-consistent polarization density functional theory (SCP-DFT). With minimal parametrization, SCP-DFT is found to give excellent results for the dimer interaction energy, the second virial coefficient, the liquid structure, and the lattice constant and cohesion energy of the face-centered cubic crystal compared to both accurate theoretical and experimental benchmarks. Thus, SCP-DFT holds promise as a fast, efficient, and accurate method for performing ab initio dynamics that include additional polarization and dispersion interactions for large, complex systems involving solvation and bond breaking.